Introduction
The global real estate market is a complex and dynamic ecosystem that is influenced by a multitude of economic factors. Whether one is an investor seeking profitable opportunities, a homeowner aiming for a long-term investment, or a developer looking to expand portfolios internationally, understanding the broader economic environment is crucial. Global economic factors such as inflation, interest rates, currency fluctuations, geopolitical tensions, and public debt directly impact property markets, shaping investment decisions, buyer behavior, and market growth. As the leading international property platform connecting buyers and sellers across over 100 countries, Primo House provides insights into how these economic dynamics influence real estate markets worldwide.
The year 2025 has brought a unique set of challenges and opportunities for global real estate. Rapid technological innovations, coupled with shifting economic landscapes, have redefined how people view property ownership and investment. This article explores the key global economic factors affecting real estate and offers an in-depth analysis of their implications for buyers, sellers, and investors globally.
1. Inflation: Driving Costs and Property Values
Inflation is one of the most significant economic factors influencing real estate markets. Simply put, inflation refers to the rise in prices of goods and services over time, which can impact both the cost of constructing new properties and the purchasing power of potential buyers.
Construction Costs and Property Prices
Inflation tends to increase the cost of raw materials, labor, and other essential components of construction. As prices rise, developers often pass these additional costs to buyers in the form of higher property prices. For example, the cost of steel, cement, and other building materials has consistently shown volatility in response to global supply chain disruptions and rising energy prices. As a result, real estate projects may experience delays, higher costs, or both, which in turn influences property market pricing.
From an investor’s perspective, periods of moderate inflation can be beneficial as property values generally rise along with inflation, preserving the investment’s purchasing power. However, hyperinflation or uncontrolled inflation can destabilize markets, reduce affordability, and deter investment in both residential and commercial properties.
Impact on Rental Income
Inflation not only affects property acquisition costs but also rental yields. As the cost of living increases, tenants may face higher rental demands, influencing property owners to adjust rent prices accordingly. In regions with strong demand for rental properties, this can result in increased rental income, making real estate a lucrative investment during periods of moderate inflation.
Inflation Hedging through Real Estate
Historically, real estate has been viewed as a hedge against inflation. Unlike other assets that may lose value when inflation rises, property values and rental income generally trend upwards, maintaining investor returns. This makes real estate a strategic asset for long-term portfolio growth, particularly for those investing internationally through platforms like Primo House.
2. Interest Rates: The Cost of Borrowing
Interest rates are another key economic factor that significantly shapes real estate markets. Central banks use interest rates to regulate economic growth, manage inflation, and stabilize financial systems. Changes in interest rates have direct consequences for mortgage affordability, borrowing costs, and investor sentiment.
Mortgage Rates and Affordability
When central banks raise interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive. Higher mortgage rates lead to higher monthly payments for homebuyers, reducing affordability and slowing property demand. Conversely, when interest rates are lowered, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging property purchases and boosting market activity. This dynamic directly affects residential markets and is especially relevant in international property investments where foreign buyers rely on financing options.
Investment Decisions and Market Activity
For investors, interest rates influence returns on property investments. Low interest rates can stimulate real estate investment by reducing financing costs, while high rates can suppress market activity. Additionally, interest rates impact investor preferences between different types of properties. For example, in a high-rate environment, commercial real estate with stable rental income may become more attractive than speculative residential projects.
Regional Variations in Interest Rates
Global real estate markets experience diverse interest rate trends. Developed economies often have more stable and predictable rates, while emerging markets may see higher volatility. For instance, some countries maintain high rates to curb inflation, while others adopt lower rates to stimulate economic growth. International investors must assess these differences carefully when exploring properties across borders.
3. Currency Fluctuations: Cross-Border Investments
For international real estate transactions, currency fluctuations are a critical consideration. Exchange rate volatility can significantly impact the affordability and profitability of buying property abroad.
Buying Power and Exchange Rates
When a buyer’s home currency strengthens against the target market’s currency, foreign property becomes more affordable. Conversely, if the home currency weakens, the cost of international property rises, potentially deterring investment. For example, investors looking to purchase property in Europe or Asia need to monitor currency trends to maximize their purchasing power.
Hedging Against Currency Risk
Many investors use hedging strategies to mitigate currency risk. These can include forward contracts, options, or choosing properties in countries with stable currencies. Platforms like Primo House facilitate cross-border transactions and provide guidance for buyers to navigate currency fluctuations, making international property investment safer and more accessible.
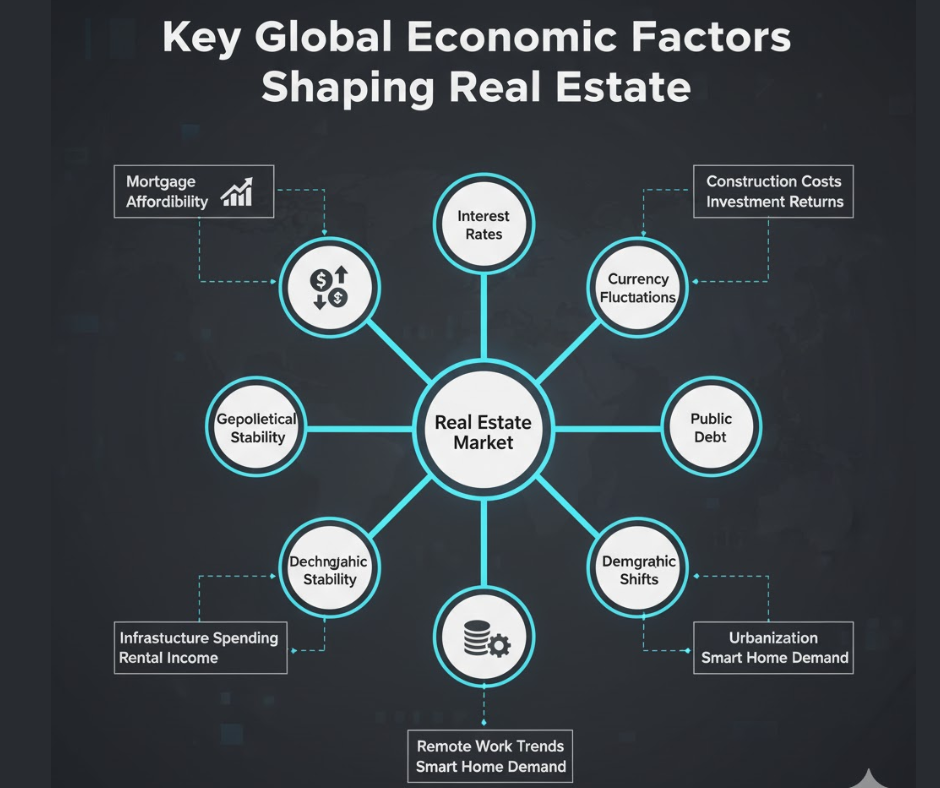
4. Geopolitical Tensions: Uncertainty and Risk
Political and geopolitical developments are often underestimated factors in global real estate markets. Trade disputes, political instability, regulatory changes, and conflicts can create uncertainty, affecting investment decisions and market growth.
Trade Disputes and Economic Stability
Trade tensions between major economies can influence property markets indirectly. For instance, disruptions in global supply chains can increase construction costs, delay projects, or create uncertainty for developers. Similarly, restrictions on foreign investment in certain countries may limit property access for international buyers.
Political Instability and Investor Confidence
Countries experiencing political instability or civil unrest often see a reduction in real estate investment. Investors prefer markets with predictable legal frameworks and stable governance. As a result, real estate in politically stable countries often becomes a safe haven for both domestic and international investors.
Opportunities Amidst Uncertainty
While geopolitical risks can deter investment, they can also create opportunities. Properties in regions perceived as safe or economically resilient may experience increased demand, driving up prices and rental yields. For example, international buyers often seek properties in countries with strong legal protections and robust economic policies during periods of global uncertainty.
5. Public Debt Levels: Government Spending and Infrastructure
Rising public debt can affect real estate markets indirectly through its impact on government spending, infrastructure development, and economic stability.
Fiscal Policies and Infrastructure
Governments with high debt levels may have limited fiscal flexibility to invest in infrastructure projects, which are critical for real estate development. Infrastructure such as roads, public transit, and utilities significantly enhances property values and market attractiveness. Conversely, countries with sound fiscal policies and strategic investments tend to foster vibrant property markets.
Borrowing Costs and Investment
High public debt often leads to higher borrowing costs for governments, which can trickle down to private borrowers. As borrowing costs rise, real estate development may slow, affecting property supply and long-term market growth. International investors must assess a country’s debt situation to gauge potential risks and opportunities in the real estate market.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
United States
The U.S. real estate market remains one of the most influential globally. In recent years, it has experienced steady growth in urban centers, driven by employment opportunities, economic stability, and technological innovation. However, rising mortgage rates and affordability challenges have slightly tempered growth, particularly in the residential sector. Investors focusing on commercial real estate are increasingly looking at sectors such as logistics and warehousing due to the rise of e-commerce.
Europe
European property markets show diverse trends across regions. Western Europe benefits from strong legal protections, transparent markets, and consistent demand for residential and commercial properties. Eastern Europe, on the other hand, presents growth opportunities but comes with higher volatility. Interest rates, currency stability, and economic policies remain key factors influencing investor decisions in these markets.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is one of the fastest-growing real estate markets globally. Urbanization, technological advancements, and a growing middle class drive residential and commercial property demand. Markets such as Singapore, Japan, and South Korea offer stability and transparency, while emerging markets like India, Indonesia, and Vietnam provide high-growth potential. Economic policies, interest rates, and infrastructure development play pivotal roles in shaping market performance.
Middle East and Africa
In the Middle East, real estate markets are influenced by oil prices, economic diversification efforts, and foreign investment policies. African markets present long-term growth potential due to demographic expansion and urban development, but political and economic instability can affect investment confidence. Investors are increasingly selective, focusing on countries with strong governance and market transparency.
7. Global Economic Recovery Post-Pandemic
The post-pandemic global economy has reshaped real estate markets in several ways:
- Shift to Remote Work: Remote work has altered residential property preferences, with buyers seeking larger homes and suburban or rural locations.
- Logistics and Warehousing Boom: E-commerce growth has driven demand for logistics and warehousing spaces globally.
- Healthcare and Senior Living: Aging populations in developed countries have increased demand for healthcare facilities and senior living communities.
Understanding these macroeconomic shifts helps investors and buyers align their strategies with emerging market trends.
8. Real Estate as a Strategic Investment
Despite the challenges posed by global economic factors, real estate remains a strategic investment vehicle for several reasons:
- Tangible Asset: Unlike stocks or bonds, real estate is a physical asset that retains intrinsic value.
- Income Generation: Rental properties provide steady cash flow, offering financial security during volatile economic periods.
- Diversification: International property investment diversifies portfolios, reducing overall risk exposure.
- Inflation Hedge: Property values and rental income generally increase with inflation, preserving wealth over time.
Platforms like Primo House make it easier for global investors to access diverse property markets, providing tools and insights to make informed investment decisions.

9. Strategies for Navigating Economic Influences
To succeed in international real estate amid global economic fluctuations, investors should consider the following strategies:
- Market Research: Study macroeconomic indicators, currency trends, and geopolitical risks before investing.
- Diversification: Spread investments across countries, property types, and risk profiles.
- Long-Term Perspective: Real estate is generally a long-term investment; avoid short-term speculation.
- Leverage Technology: Use property platforms to access real-time market data and opportunities.
- Professional Advice: Consult with legal, financial, and real estate experts to navigate complex international markets.
Conclusion
Global economic factors—ranging from inflation and interest rates to geopolitical risks and public debt—have a profound influence on real estate markets worldwide. Understanding these dynamics is essential for investors, buyers, and developers to make informed decisions and maximize returns. While challenges exist, strategic planning, market research, and leveraging international property platforms like Primo House can unlock significant opportunities in global real estate.
As the world continues to evolve economically and technologically, staying informed about global economic trends remains crucial. Whether investing in residential, commercial, or luxury international properties, knowledge of economic factors ensures smarter, more resilient real estate decisions.
Primo House empowers investors and buyers with access to properties in over 100 countries, offering the tools and insights necessary to navigate the complexities of global real estate markets with confidence.





